Commands¶
Introduction¶
greenmask \
--log-format=[json|text] \
--log-level=[debug|info|error] \
--config=config.yml \
[dump|list-dumps|delete|list-transformers|show-transformer|restore|show-dump]`
You can use the following commands within Greenmask:
dump— initiates the data dumping processlist-dumps— lists all available dumps stored in the systemdelete— deletes a specific dump from the storagelist-transformers— displays a list of available transformers along with their documentationshow-transformer— displays information about the specified transformerrestore— restores data to the target database either by specifying adumpIdor using the latest available dumpshow-dump— provides metadata information about a particular dump, offering insights into its structure and attributes
For any of the commands mentioned above, you can include the following common flags:
--log-format— specifies the desired format for log output, which can be eitherjsonortext. This parameter is optional, with the default format set totext.--log-level— sets the desired level for log output, which can be one ofdebug,info, orerror. This parameter is optional, with the default log level beinginfo.--config— requires the specification of a configuration file in YAML format. This configuration file is mandatory for Greenmask to operate correctly.--help— displays comprehensive help information for Greenmask, providing guidance on its usage and available commands.
validate¶
The validate command allows you to perform a validation procedure and compare data transformations.
Below is a list of all supported flags for the validate command:
Usage:
greenmask validate [flags]
Flags:
--data Perform test dump for --rows-limit rows and print it pretty
--diff Find difference between original and transformed data
--format string Format of output. possible values [text|json] (default "text")
--rows-limit uint Check tables dump only for specific tables (default 10)
--schema Make a schema diff between previous dump and the current state
--table strings Check tables dump only for specific tables
--table-format string Format of table output (only for --format=text). Possible values [vertical|horizontal] (default "vertical")
--transformed-only Print only transformed column and primary key
--warnings Print warnings
Validate command can exit with non-zero code when:
- Any error occurred
- Validate was called with
--waringsflag and there are warnings - Validate was called with
--schemaflag and there are schema differences
All of those cases may be used for CI/CD pipelines to stop the process when something went wrong. This is especially
useful when --schema flag is used - this allows to avoid data leakage when schema changed.
You can use the --table flag multiple times to specify the tables you want to check. Tables can be written with
or without schema names (e. g., public.table_name or table_name). If you specify multiple tables from different
schemas, an error will be thrown.
To start validation, use the following command:
greenmask --config=config.yml validate \
--warnings \
--data \
--diff \
--schema \
--format=text \
--table-format=vertical \
--transformed-only \
--rows-limit=1
2024-03-15T19:46:12+02:00 WRN ValidationWarning={"hash":"aa808fb574a1359c6606e464833feceb","meta":{"ColumnName":"birthdate","ConstraintDef":"CHECK (birthdate \u003e= '1930-01-01'::date AND birthdate \u003c= (now() - '18 years'::interval))","ConstraintName":"humanresources","ConstraintSchema":"humanresources","ConstraintType":"Check","ParameterName":"column","SchemaName":"humanresources","TableName":"employee","TransformerName":"NoiseDate"},"msg":"possible constraint violation: column has Check constraint","severity":"warning"}
The validation output will provide detailed information about potential constraint violations and schema issues. Each
line contains nested JSON data under the ValidationWarning key, offering insights into the affected part of the
configuration and potential constraint violations.
{
"hash": "aa808fb574a1359c6606e464833feceb", // (13)
"meta": { // (1)
"ColumnName": "birthdate", // (2)
"ConstraintDef": "CHECK (birthdate >= '1930-01-01'::date AND birthdate <= (now() - '18 years'::interval))", // (3)
"ConstraintName": "humanresources", // (4)
"ConstraintSchema": "humanresources", // (5)
"ConstraintType": "Check", // (6)
"ParameterName": "column", // (7)
"SchemaName": "humanresources", // (8)
"TableName": "employee", // (9)
"TransformerName": "NoiseDate" // (10)
},
"msg": "possible constraint violation: column has Check constraint", // (11)
"severity": "warning" // (12)
}
- Detailed metadata. The validation output provides comprehensive metadata to pinpoint the source of problems.
- Column name indicates the name of the affected column.
- Constraint definition specifies the definition of the constraint that may be violated.
- Constraint name identifies the name of the constraint that is potentially violated.
- Constraint schema name indicates the schema in which the constraint is defined.
- Type of constraint represents the type of constraint and can be one of the following:
* ForeignKey * Check * NotNull * PrimaryKey * PrimaryKeyReferences * Unique * Length * Exclusion * TriggerConstraint - Table schema name specifies the schema name of the affected table.
- Table name identifies the name of the table where the problem occurs.
- Transformer name indicates the name of the transformer responsible for the transformation.
- Name of affected parameter typically, this is the name of the column parameter that is relevant to the validation warning.
- Validation warning description provides a detailed description of the validation warning and the reason behind it.
- Severity of validation warning indicates the severity level of the validation warning and can be one of the
following:
* error * warning * info * debug - Hash is a unique identifier of the validation warning. It is used to resolve the warning in the config file
Note
A validation warning with a severity level of "error" is considered critical and must be addressed before the dump operation can proceed. Failure to resolve such warnings will prevent the dump operation from being executed.
2024-03-15T19:46:12+02:00 WRN Database schema has been changed Hint="Check schema changes before making new dump" PreviousDumpId=1710520855501
2024-03-15T19:46:12+02:00 WRN Column renamed Event=ColumnRenamed Signature={"CurrentColumnName":"id1","PreviousColumnName":"id","TableName":"test","TableSchema":"public"}
2024-03-15T19:46:12+02:00 WRN Column type changed Event=ColumnTypeChanged Signature={"ColumnName":"id","CurrentColumnType":"bigint","CurrentColumnTypeOid":"20","PreviousColumnType":"integer","PreviousColumnTypeOid":"23","TableName":"test","TableSchema":"public"}
2024-03-15T19:46:12+02:00 WRN Column created Event=ColumnCreated Signature={"ColumnName":"name","ColumnType":"text","TableName":"test","TableSchema":"public"}
2024-03-15T19:46:12+02:00 WRN Table created Event=TableCreated Signature={"SchemaName":"public","TableName":"test1","TableOid":"20563"}
Example of validation diff:
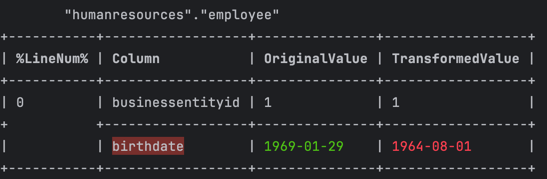
The validation diff is presented in a neatly formatted table. In this table:
- Columns that are affected by the transformation are highlighted with a red background.
- The pre-transformation values are displayed in green.
- The post-transformation values are shown in red.
- The result in
--format=textcan be displayed in either horizontal (--table-format=horizontal) or vertical (--table-format=vertical) format, making it easy to visualize and understand the differences between the original and transformed data.
The whole validate command may be run in json format including logging making easy to parse the structure.
greenmask --config=config.yml validate \
--warnings \
--data \
--diff \
--schema \
--format=json \
--table-format=vertical \
--transformed-only \
--rows-limit=1 \
--log-format=json
The json object result
{
"level": "warn",
"ValidationWarning": {
"msg": "possible constraint violation: column has Check constraint",
"severity": "warning",
"meta": {
"ColumnName": "birthdate",
"ConstraintDef": "CHECK (birthdate >= '1930-01-01'::date AND birthdate <= (now() - '18 years'::interval))",
"ConstraintName": "humanresources",
"ConstraintSchema": "humanresources",
"ConstraintType": "Check",
"ParameterName": "column",
"SchemaName": "humanresources",
"TableName": "employee",
"TransformerName": "NoiseDate"
},
"hash": "aa808fb574a1359c6606e464833feceb"
},
"time": "2024-03-15T20:01:51+02:00"
}
{
"level": "warn",
"PreviousDumpId": "1710520855501",
"Diff": [
{
"event": "ColumnRenamed",
"signature": {
"CurrentColumnName": "id1",
"PreviousColumnName": "id",
"TableName": "test",
"TableSchema": "public"
}
},
{
"event": "ColumnTypeChanged",
"signature": {
"ColumnName": "id",
"CurrentColumnType": "bigint",
"CurrentColumnTypeOid": "20",
"PreviousColumnType": "integer",
"PreviousColumnTypeOid": "23",
"TableName": "test",
"TableSchema": "public"
}
},
{
"event": "ColumnCreated",
"signature": {
"ColumnName": "name",
"ColumnType": "text",
"TableName": "test",
"TableSchema": "public"
}
},
{
"event": "TableCreated",
"signature": {
"SchemaName": "public",
"TableName": "test1",
"TableOid": "20563"
}
}
],
"Hint": "Check schema changes before making new dump",
"time": "2024-03-15T20:01:51+02:00",
"message": "Database schema has been changed"
}
{
"schema": "humanresources",
"name": "employee",
"primary_key_columns": [
"businessentityid"
],
"with_diff": true,
"transformed_only": true,
"records": [
{
"birthdate": {
"original": "1969-01-29",
"transformed": "1964-10-20",
"equal": false,
"implicit": true
},
"businessentityid": {
"original": "1",
"transformed": "1",
"equal": true,
"implicit": true
}
}
]
}
dump¶
The dump command operates in the following way:
- Dumps the data from the source database.
- Validates the data for potential issues.
- Applies the defined transformations.
- Stores the transformed data in the specified storage location.
Usage:
greenmask dump [flags]
Flags:
-b, --blobs include large objects in dump
-c, --clean clean (drop) database objects before recreating
-Z, --compress int compression level for compressed formats (default -1)
-C, --create include commands to create database in dump
-a, --data-only dump only the data, not the schema
-d, --dbname string database to dump (default "postgres")
--disable-dollar-quoting disable dollar quoting, use SQL standard quoting
--disable-triggers disable triggers during data-only restore
--enable-row-security enable row security (dump only content user has access to)
-E, --encoding string dump the data in encoding ENCODING
-N, --exclude-schema strings dump the specified schema(s) only
-T, --exclude-table strings do NOT dump the specified table(s)
--exclude-table-data strings do NOT dump data for the specified table(s)
-e, --extension strings dump the specified extension(s) only
--extra-float-digits string override default setting for extra_float_digits
-f, --file string output file or directory name
-h, --host string database server host or socket directory (default "/var/run/postgres")
--if-exists use IF EXISTS when dropping objects
--include-foreign-data strings use IF EXISTS when dropping objects
-j, --jobs int use this many parallel jobs to dump (default 1)
--load-via-partition-root load partitions via the root table
--lock-wait-timeout int fail after waiting TIMEOUT for a table lock (default -1)
-B, --no-blobs exclude large objects in dump
--no-comments do not dump comments
-O, --no-owner string skip restoration of object ownership in plain-text format
-X, --no-privileges do not dump privileges (grant/revoke)
--no-publications do not dump publications
--no-security-labels do not dump security label assignments
--no-subscriptions do not dump subscriptions
--no-sync do not wait for changes to be written safely to dis
--no-synchronized-snapshots do not use synchronized snapshots in parallel jobs
--no-tablespaces do not dump tablespace assignments
--no-toast-compression do not dump TOAST compression methods
--no-unlogged-table-data do not dump unlogged table data
--on-conflict-do-nothing add ON CONFLICT DO NOTHING to INSERT commands
-p, --port int database server port number (default 5432)
--quote-all-identifiers quote all identifiers, even if not key words
-n, --schema strings dump the specified schema(s) only
-s, --schema-only string dump only the schema, no data
--section string dump named section (pre-data, data, or post-data)
--serializable-deferrable wait until the dump can run without anomalies
--snapshot string use given snapshot for the dump
--strict-names require table and/or schema include patterns to match at least one entity each
-S, --superuser string superuser user name to use in plain-text format
-t, --table strings dump the specified table(s) only
--test string connect as specified database user (default "postgres")
--use-set-session-authorization use SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION commands instead of ALTER OWNER commands to set ownership
-U, --username string connect as specified database user (default "postgres")
-v, --verbose string verbose mode
list-dumps¶
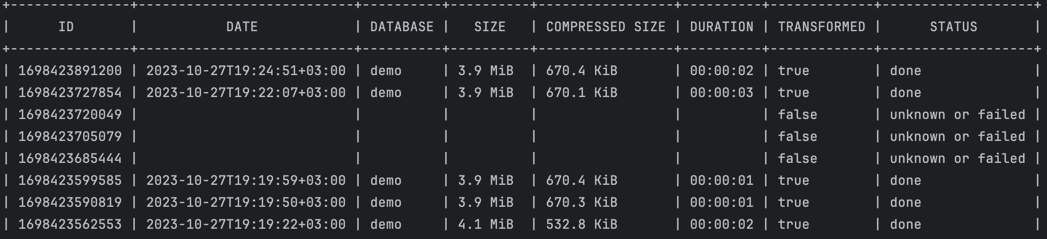
The list-dumps command provides a list of all dumps stored in the storage. The list includes the following attributes:
ID— the unique identifier of the dump, used for operations likerestore,delete, andshow-dumpDATE— the date when the snapshot was createdDATABASE— the name of the database associated with the dumpSIZE— the original size of the dumpCOMPRESSED SIZE— the size of the dump after compressionDURATION— the duration of the dump procedureTRANSFORMED— indicates whether the dump has been transformedSTATUS— the status of the dump, which can be one of the following:done— the dump was completed successfullyunknownorfailed— the dump might be in progress or failed. Failed dumps are not deleted automatically.
Example of list-dumps output:
list-transformers¶
The list-transformers command provides a list of all the allowed transformers, including both standard and advanced
transformers. This list can be helpful for searching for an appropriate transformer for your data transformation needs.
To show a list of available transformers, use the following command:
greenmask --config=config.yml list-transformers
Supported flags:
--format— allows to select the output format. There are two options available:textorjson. The default setting istext.
Example of list-transformers output:
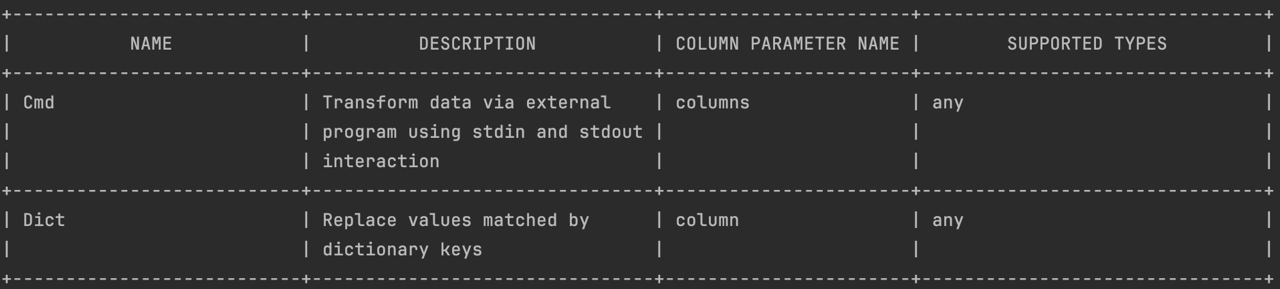
When using the list-transformers command, you receive a list of available transformers with essential information
about each of them. Below are the key parameters for each transformer:
NAME— the name of the transformerDESCRIPTION— a brief description of what the transformer doesCOLUMN PARAMETER NAME— name of a column or columns affected by transformationSUPPORTED TYPES— list the supported value types
The JSON call greenmask --config=config.yml list-transformers --format=json has the same attributes:
[
{
"name": "Cmd",
"description": "Transform data via external program using stdin and stdout interaction",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "columns",
"supported_types": [
"any"
]
}
]
},
{
"name": "Dict",
"description": "Replace values matched by dictionary keys",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "column",
"supported_types": [
"any"
]
}
]
}
]
show-transformer¶
This command prints out detailed information about a transformer by a provided name, including specific attributes to help you understand and configure the transformer effectively.
To show detailed information about a transformer, use the following command:
greenmask --config=config.yml show-transformer TRANSFORMER_NAME
Supported flags:
--format— allows to select the output format. There are two options available:textorjson. The default setting istext.
Example of show-transformer output:
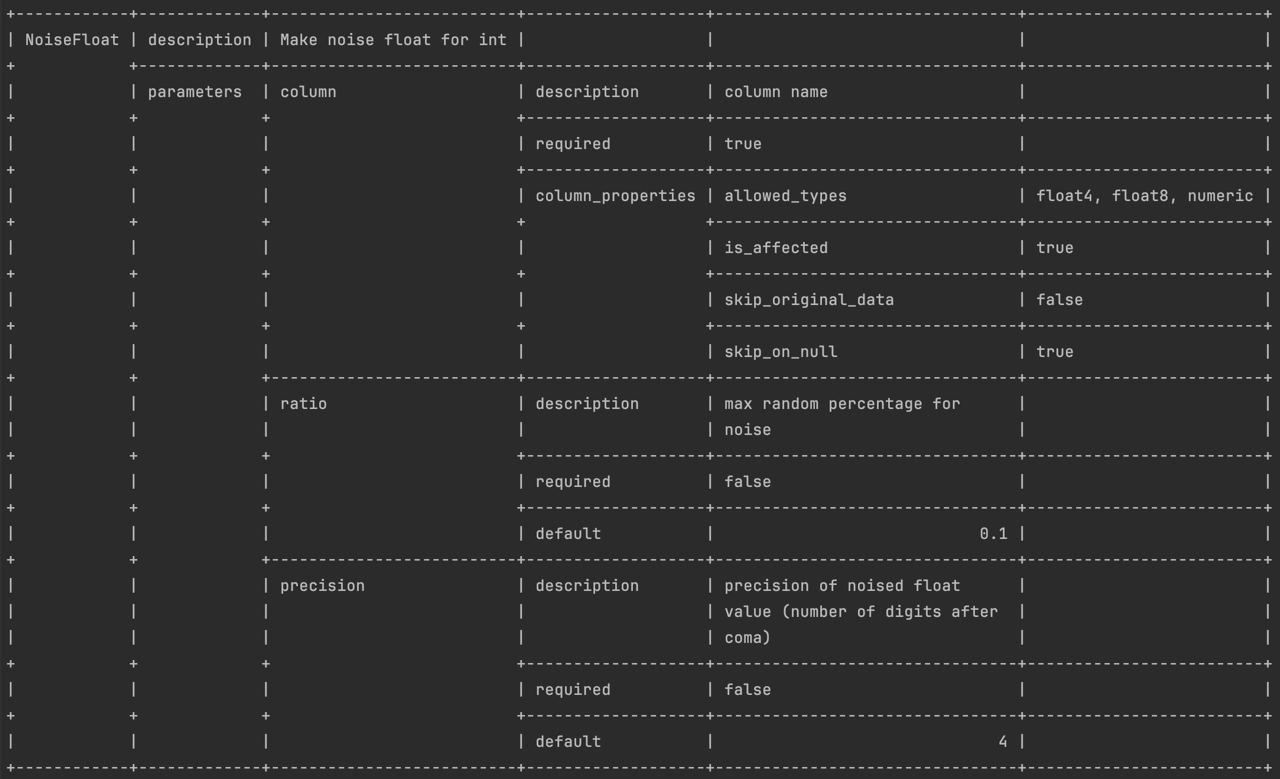
When using the show-transformer command, you receive detailed information about the transformer and its parameters and
their possible attributes. Below are the key parameters for each transformer:
Name— the name of the transformerDescription— a brief description of what the transformer does-
Parameters— a list of transformer parameters, each with its own set of attributes. Possible attributes include:description— a brief description of the parameter's purposerequired— a flag indicating whether the parameter is required when configuring the transformerlink_parameter— specifies whether the value of the parameter will be encoded using a specific parameter type encoder. For example, if a parameter namedcolumnis linked to another parameterstart, thestartparameter's value will be encoded according to thecolumntype when the transformer is initialized.cast_db_type— indicates that the value should be encoded according to the database type. For example, when dealing with the INTERVAL data type, you must provide the interval value in PostgreSQL format.default_value— the default value assigned to the parameter if it's not provided during configuration.column_properties— if a parameter represents the name of a column, it may contain additional properties, including:nullable— indicates whether the transformer may produce NULL values, potentially violating the NOT NULL constraintunique— specifies whether the transformer guarantees unique values for each call. If set totrue, it means that the transformer cannot produce duplicate values, ensuring compliance with the UNIQUE constraint.affected— indicates whether the column is affected during the transformation process. If not affected, the column's value might still be required for transforming another column.allowed_types— a list of data types that are compatible with this parameterskip_original_data— specifies whether the original value of the column, before transformation, is relevant for the transformation processskip_on_null— indicates whether the transformer should skip the transformation when the input column value is NULL. If the column value is NULL, interaction with the transformer is unnecessary.
Warning
The default value in JSON format is base64 encoded. This might be changed in later version of Greenmask.
[
{
"properties": {
"name": "NoiseFloat",
"description": "Make noise float for int",
"is_custom": false
},
"parameters": [
{
"name": "column",
"description": "column name",
"required": true,
"is_column": true,
"is_column_container": false,
"column_properties": {
"max_length": -1,
"affected": true,
"allowed_types": [
"float4",
"float8",
"numeric"
],
"skip_on_null": true
}
},
{
"name": "ratio",
"description": "max random percentage for noise",
"required": false,
"is_column": false,
"is_column_container": false,
"default_value": "MC4x"
},
{
"name": "precision",
"description": "precision of noised float value (number of digits after coma)",
"required": false,
"is_column": false,
"is_column_container": false,
"default_value": "NA=="
}
]
}
]
restore¶
To perform a dump restoration with the provided dump ID, use the following command:
greenmask --config=config.yml restore DUMP_ID
Alternatively, to restore the latest completed dump, use the following command:
greenmask --config=config.yml restore latest
Note that the restore command shares the same parameters and environment variables as pg_restore,
allowing you to configure the restoration process as needed.
Flags:
-c, --clean clean (drop) database objects before recreating
-C, --create create the target database
-a, --data-only restore only the data, no schema
-d, --dbname string connect to database name (default "postgres")
--disable-triggers disable triggers during data-only restore
--enable-row-security enable row security
-N, --exclude-schema strings do not restore objects in this schema
-e, --exit-on-error exit on error, default is to continue
-f, --file string output file name (- for stdout)
-P, --function strings restore named function
-h, --host string database server host or socket directory (default "/var/run/postgres")
--if-exists use IF EXISTS when dropping objects
-i, --index strings restore named index
-j, --jobs int use this many parallel jobs to restore (default 1)
--list-format string use table of contents in format of text, json or yaml (default "text")
--no-comments do not restore comments
--no-data-for-failed-tables do not restore data of tables that could not be created
-O, --no-owner string skip restoration of object ownership
-X, --no-privileges skip restoration of access privileges (grant/revoke)
--no-publications do not restore publications
--no-security-labels do not restore security labels
--no-subscriptions ddo not restore subscriptions
--no-table-access-method do not restore table access methods
--no-tablespaces do not restore tablespace assignments
-p, --port int database server port number (default 5432)
-n, --schema strings restore only objects in this schema
-s, --schema-only string restore only the schema, no data
--section string restore named section (pre-data, data, or post-data)
-1, --single-transaction restore as a single transaction
--strict-names restore named section (pre-data, data, or post-data) match at least one entity each
-S, --superuser string superuser user name to use for disabling triggers
-t, --table strings restore named relation (table, view, etc.)
-T, --trigger strings restore named trigger
-L, --use-list string use table of contents from this file for selecting/ordering output
--use-set-session-authorization use SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION commands instead of ALTER OWNER commands to set ownership
-U, --username string connect as specified database user (default "postgres")
-v, --verbose string verbose mode
show-dump¶
This command provides details about all objects and data that can be restored, similar to the pg_restore -l command in
PostgreSQL. It helps you inspect the contents of the dump before performing the actual restoration.
Parameters:
--format— format of printing. Can betextorjson.
To display metadata information about a dump, use the following command:
greenmask --config=config.yml show-dump dumpID
;
; Archive created at 2023-10-30 12:52:38 UTC
; dbname: demo
; TOC Entries: 17
; Compression: -1
; Dump Version: 15.4
; Format: DIRECTORY
; Integer: 4 bytes
; Offset: 8 bytes
; Dumped from database version: 15.4
; Dumped by pg_dump version: 15.4
;
;
; Selected TOC Entries:
;
3444; 0 0 ENCODING - ENCODING
3445; 0 0 STDSTRINGS - STDSTRINGS
3446; 0 0 SEARCHPATH - SEARCHPATH
3447; 1262 24970 DATABASE - demo postgres
3448; 0 0 DATABASE PROPERTIES - demo postgres
222; 1259 24999 TABLE bookings flights postgres
223; 1259 25005 SEQUENCE bookings flights_flight_id_seq postgres
3460; 0 0 SEQUENCE OWNED BY bookings flights_flight_id_seq postgres
3281; 2604 25030 DEFAULT bookings flights flight_id postgres
3462; 0 24999 TABLE DATA bookings flights postgres
3289; 2606 25044 CONSTRAINT bookings flights flights_flight_no_scheduled_departure_key postgres
3291; 2606 25046 CONSTRAINT bookings flights flights_pkey postgres
3287; 1259 42848 INDEX bookings flights_aircraft_code_status_idx postgres
3292; 1259 42847 INDEX bookings flights_status_aircraft_code_idx postgres
3293; 2606 25058 FK CONSTRAINT bookings flights flights_aircraft_code_fkey postgres
3294; 2606 25063 FK CONSTRAINT bookings flights flights_arrival_airport_fkey postgres
3295; 2606 25068 FK CONSTRAINT bookings flights flights_departure_airport_fkey postgres
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 | |
- The date when the backup has been initiated, also indicating the snapshot date.
- The date when the backup process was successfully completed.
- The original size of the backup in bytes.
- The size of the backup after compression in bytes.
- A list of tables that underwent transformation during the backup.
- The schema name of the table.
- The name of the table.
- Custom query override, if applicable.
- A list of transformers that were applied during the backup.
- The name of the transformer.
- The parameters provided for the transformer.
- A mapping of overridden column types.
- The header information in the table of contents file. This provides the same details as the
--format=textoutput in the previous snippet. - The list of restoration entries. This offers the same information as the
--format=textoutput in the previous snippet.
Note
The json format provides more detailed information compared to the text format. The text format is primarily used for backward compatibility and for generating a restoration list that can be used with pg_restore -L listfile. On the other hand, the json format provides comprehensive metadata about the dump, including information about the applied transformers and their parameters. The json format is especially useful for detailed dump introspection.